Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of the trucking industry, understanding economic trends is not just beneficial; it is essential. As freight volumes fluctuate and tariffs impose new challenges, industry professionals must equip themselves with the nuances of the market to make informed decisions. Recent shifts in both the U.S. and Canadian trucking sectors have underscored the interconnectedness of these markets, highlighting how changes in one can significantly impact the other.
With a cautious yet analytical approach, this article aims to dissect the current economic landscape, providing insights that will empower stakeholders to navigate the complexities of today’s trucking market. Recognizing these trends is crucial for forecasting demand, optimizing operations, and ultimately ensuring competitive advantage in a challenging environment.
Improving Trends in Freight Volumes
As we delve deeper into the current state of the trucking market, it is important to acknowledge the positive signs emerging amidst ongoing challenges. Notably, as reported, U.S. for-hire truck tonnage rose by 0.9% in August, following a 1.1% rise in July. Furthermore, year-to-date tonnage is up 0.1% compared to the same period last year, highlighting a trend of cautious improvement.
One of the key voices in this discussion is Bob Costello, the chief economist at the American Trucking Associations, who remarked, “The good news is that truck freight volumes had a nice end of the summer.” This statement underscores the emerging confidence in freight demand as we shift into the fall months. Such insights are valuable for industry observers and stakeholders, emphasizing the necessity of vigilance and adaptability in this fluctuating market.
Improving Trends in Freight Volumes
As we explore the current trucking market, we see some positive changes despite ongoing challenges. U.S. for-hire truck tonnage rose by 0.9% in August after a 1.1% rise in July. Year-to-date tonnage is also up by 0.1% compared to the same period last year. This shows a cautious improvement.
Bob Costello, chief economist at the American Trucking Associations, shared a hopeful perspective. He said, “The good news is that truck freight volumes had a nice end of the summer.” This statement reflects a growing confidence in freight demand as we transition into fall. Stakeholders and observers should take note of these insights, emphasizing the importance of being adaptable in this changing market.
Summary of FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index Improvement
FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index (TCI) saw a slight bounce from June to July 2023. It improved from -6.29 to -5.34, indicating a minor easing of challenging market conditions. The increase in TCI arose mainly due to better freight volumes and capacity utilization, which helped counterbalance issues like low freight rates and rising fuel prices.
The TCI acts as a crucial indicator for the trucking industry. It reflects various economic elements such as freight volumes, rates, and fuel costs. Despite the upward trend, the index remains negative, revealing ongoing pressures, particularly for smaller carriers coping with higher fuel prices. The larger carriers have absorbed some of this market capacity, yet overall conditions remain sluggish, influenced by diminished freight demand.
Bob Costello noted, “The good news is that truck freight volumes had a nice end of the summer,” showcasing strengthened freight activity. However, Tim Denoyer from ACT Research cautioned that “our freight demand outlook remains cautious,” suggesting that while things appear to be improving a bit, challenges are still present.
In summary, while the TCI has slightly improved, the trucking industry continues to face a reality filled with fuel price volatility, demand shifts, and other economic uncertainties. Stakeholders need to remain adaptable and vigilant to navigate this complex landscape.
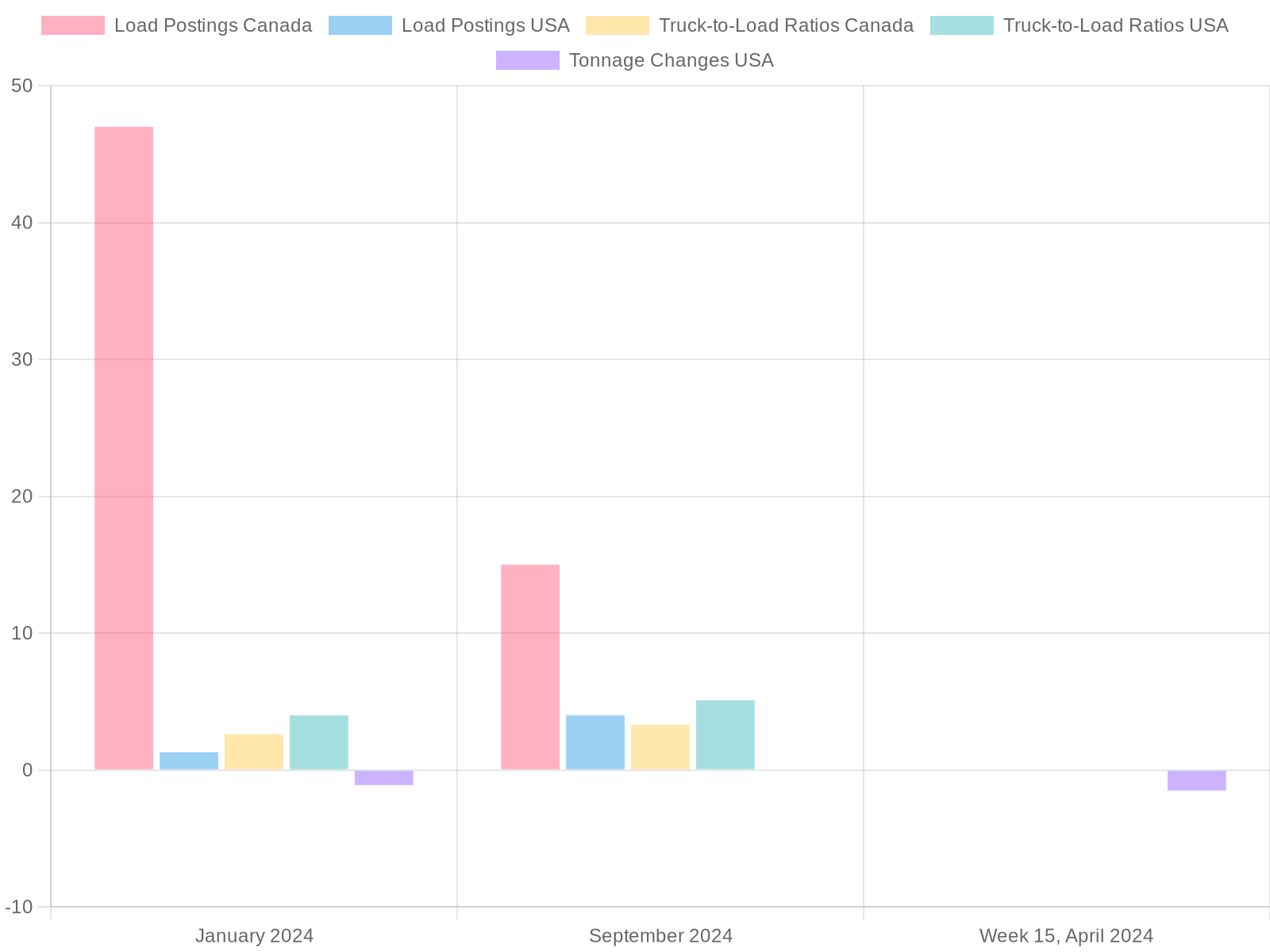
| Metric | Canada | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Load Postings |
|
|
| Truck-to-Load Ratios |
|
|
| Tonnage Changes |
|
|
Sources:
- Canada:
- Loadlink Technologies, “Loadlink’s Canadian Spot Market Achieves Remarkable 47% Increase in Load Volumes to Kick Off 2024” [loadlink.ca]
- Loadlink Technologies, “Shifting Dynamic: A Return to a Trucker’s Market?” [loadlink.ca]
- United States:
- FleetOwner, “Mixed freight changes in latest DAT, FTR market data” [fleetowner.com]
- IRU, “US truck tonnage contracted 1.1% in December” [iru.org]
- American Trucking Associations, “ATA Truck Tonnage Index Unchanged in January” [trucking.org]
- American Trucking Associations, “ATA Truck Tonnage Index Declined 1.5% in March” [trucking.org]
Summary of FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index Improvement
In a critical examination of the trucking industry, FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index (TCI) showed a slight improvement from June to July 2023, climbing from -6.29 to -5.34. This marginal enhancement indicates a minor easing of unfavorable market conditions. Primarily, the uptick in the TCI was attributed to improved freight volumes and capacity utilization, which helped offset the challenges associated with weak freight rates and escalating fuel costs.
The TCI serves as a barometer for the trucking industry, reflecting various economic factors such as freight volumes, rates, fuel prices, and market dynamics. Despite the positive change, the index remains in negative territory, underscoring the continued difficulties faced by carriers. The persistent negative readings highlight the substantial pressures on the trucking industry, particularly for smaller operators who are struggling with rising fuel expenses. Many small carriers are exiting the market, burdened by these costs and the adverse economic climate. Larger carriers have absorbed some of this capacity, yet the market overall remains sluggish, weakly buoyed by diminished freight demand.
The implications for the trucking industry are significant. With the TCI’s mild improvement, there may be a glimmer of hope for stakeholders assessing the state of freight volumes and market stability. Bob Costello, chief economist at the American Trucking Associations, noted, “The good news is that truck freight volumes had a nice end of the summer,” indicating strengthened freight activity. However, Tim Denoyer, vice president and senior analyst at ACT Research, cautioned that “our freight demand outlook remains cautious,” suggesting that while conditions appear to be stabilizing slightly, challenges are far from resolved.
In conclusion, while the improvement in FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index from June to July 2023 suggests a modest easing of challenges within the trucking sector, the industry continues to navigate a complex landscape marked by volatility in fuel prices, freight demand, and overall economic conditions. Stakeholders must remain vigilant and adaptable, ready to respond to fluctuating market dynamics to safeguard their operations and maintain competitiveness in a challenging environment.
Class 8 Orders: Recent Trends and Challenges
The Class 8 truck segment is facing significant headwinds as recent data highlight a concerning decline in orders, primarily driven by tariff-related pressures and broader economic challenges. In July 2025, there was a notable 7% year-over-year decrease in Class 8 truck orders, marking the seventh consecutive annual decline. The net orders have decreased by 30% year-to-date, illustrating a broader pattern of uncertainty in the market [source].
An analysis of the economic environment reveals that the trucking industry is grappling with the implications of the U.S. government’s decision to implement a 25% tariff on medium- and heavy-duty truck imports, effective November 1, 2025. This policy is expected to hike the average cost of new heavy trucks by $25,000 to $30,000, which presents a substantial obstacle for fleet operators attempting to modernize their equipment, especially smaller carriers [source]. The American Trucking Associations (ATA) has indicated that such tariffs could negatively affect freight volumes and increase overall operational costs, particularly for the 100,000 truckers engaged in cross-border trade with Canada and Mexico [source].
The decline in Class 8 truck orders is further corroborated by data from earlier this year. Preliminary results for January 2025 showcased a staggering 28% month-over-month decrease, which continued into February with a 31% drop, amounting to just 17,000 net orders [source]. April 2025 marked an alarming low with orders plummeting to 7,400 units, underscoring the impact of tariff anxieties on business investment decisions within this crucial segment of the trucking market [source].
To mitigate the effects of rising costs due to tariffs, manufacturers are adopting various strategies. Companies such as Daimler Truck and Traton are leveraging their production facilities in Mexico to avoid tariffs under the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), thus maintaining a competitive edge. In contrast, U.S.-based manufacturers such as Paccar are experiencing significant cost premiums and losses from tariffs, which are estimated to reach $75 million in Q3 2025 [source].
In conclusion, the landscape for Class 8 truck orders is defined by declining numbers amidst a backdrop of tariffs and economic uncertainty. As market stakeholders navigate these challenges, it becomes increasingly essential to monitor the evolving dynamics to make informed strategic decisions moving forward.

In today’s discussion of the trucking industry’s current economic conditions, it’s pivotal to note the insights shared by Tim Denoyer, vice president at ACT Research. He stated,
“As the economy is likely to absorb the effects of tariffs over the next several months, our freight demand outlook remains cautious.”
This emphasizes the ongoing challenges that the industry faces as it navigates through tightening economic conditions and fluctuating demand.
Analysis of Canada’s Spot Market Decline
The Canadian trucking spot market has experienced notable challenges, illustrated by a significant 14% drop in load postings from July to August, alongside a staggering 40% decline year-over-year. This downturn is intricately linked to broader economic trends, notably those stemming from the U.S. economy, which play a pivotal role in shaping freight demand across North America.
Decline in Spot Market Metrics
In July 2025, Canada witnessed a decrease in spot market activity, with load postings declining 14% from the previous month and 40% compared to the same period last year. This dramatic decline reflects reduced freight demand, attributed to worsening economic conditions including manufacturing slowdowns and softer labor markets. The S&P Global Canada Manufacturing PMI indicated the sixth consecutive month of contraction, with output and new orders decreasing due to tariff uncertainties impacting trade with the U.S.
Additionally, employment reductions compounded these challenges, leading to a loss of 40,800 jobs in July and pushing youth unemployment to multi-year highs. Trade metrics further highlighted these downward trends, with a widening merchandise trade deficit in Canada signaling ongoing economic distress.
Comparative U.S. Economic Trends
In stark contrast, the U.S. economy reported a modest uptick in freight related activities, with for-hire truck tonnage edging up by 0.9% in August. This increase, while indicative of overall resilience, does not sufficiently enhance cross-border freight activity, which remains subdued from Canada to the U.S. The ongoing economic conditions in the U.S., characterized by weakened consumer spending and pressures from tariffs, are mirrored in Canada’s softer market, suggesting a synchronized downturn affecting both economies.
The economic landscape is further complicated by U.S. tariff impacts, which have led to reduced import volumes and heightened operational costs for businesses reliant on cross-border trade. The sluggish U.S. economic growth rates were reflected in Q1 and Q2 2025, registering only 1.5% and 1.1% growth respectively, significantly down from the previous year’s robust expansion.
Implications for Stakeholders
The pronounced decline in Canada’s spot market, juxtaposed with steady U.S. metrics, signals a pressing need for stakeholders across the trucking industry to adopt strategic responses. Addressing the supply-demand imbalances and understanding the nuances of tariff dynamics are critical for trucking companies navigating this volatile environment.
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between the Canadian and U.S. trucking markets underscores the importance of closely monitoring these economic trends. As conditions evolve, the ability to adapt and respond strategically will be essential for maintaining competitive edges in both countries’ complex freight landscapes.
Insights from Avery Vise
Avery Vise, Vice President of Trucking at FTR Transportation Intelligence, shares critical insights regarding expected future trends in the trucking industry, focusing on a cautious outlook for freight rates and volumes.
Freight Rate and Volume Trends
- Spot Rates: Vise anticipates a rise in truckload spot rates by 6.5% to 7% in 2025, following a modest 1% increase in 2024. This suggests a more dynamic rate environment in the coming year.
- Contract Rates: An approximate 2% increase in contract rates is expected for 2025, with significant year-over-year growth of about 5% by the year’s end. This reflects a cautious optimism regarding long-term contracts amidst a backdrop of uncertainty.
- Freight Volumes: Overall freight volumes are projected to grow minimally, with a slight 1.3% increase expected for 2025. This modest growth indicates that while there are fluctuations in rates, demand does not show robust expansion.
Market Challenges
- Insurance Costs: Rising insurance premiums may lead to the exit of smaller carriers from the market. Increased operational costs could pose a risk for fleet sustainability, particularly for those unable to absorb such gradual increases.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter enforcement of English proficiency standards for drivers is another concern that could exacerbate capacity challenges for the industry moving forward.
- Fuel Price Volatility: Fluctuating diesel prices are an additional factor affecting operating costs for carriers, making it essential for businesses to adapt strategy in anticipation of ongoing price changes.
Capacity Outlook
Despite expectations for a reduction in overall capacity, many small carriers remain in the market, contributing to an overhang that could prolong the rate recession. Vise’s insights emphasize the need for careful navigation through these challenging waters as carriers must remain adaptable to shifts in demand and changing costs.
In conclusion, while the trucking industry anticipates slight improvements in freight rates, it faces persistent challenges from economic uncertainties and rising operational costs, indicating a cautious outlook for the near future.
By synthesizing Vise’s insights, stakeholders can better prepare for the complexities ahead and equip themselves with strategies to maintain competitiveness in this evolving market.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the current economic trends shaping the trucking market, it becomes increasingly clear that industry professionals must maintain a pulse on the evolving landscape. The mixed signals from the U.S. and Canadian markets – including rising tonnage in the U.S. and a significant decline in Canada – underscore the interconnectedness of these economies. Additionally, the looming impact of tariffs on Class 8 orders further complicates the operational environment. Freight rates are anticipated to fluctuate modestly, prompting stakeholders to remain vigilant and adaptable in their strategies.
The cautious insights from analysts like Tim Denoyer and Avery Vise remind us that while there are signs of improvement, a prudent approach is essential for navigating potential challenges. Ultimately, staying informed about critical economic indicators, such as trucking trends, freight demand, and market conditions, and adjusting strategies accordingly will be paramount for success in the trucking industry.
Transition Statement
As we delve into the significant challenges highlighted by the improvement in FTR’s Trucking Conditions Index, it’s important to recognize that these conditions influence multiple facets of the trucking market, including the vital Class 8 orders. The economic landscape shaped by freight volume fluctuations and the impacts of tariffs creates a complex backdrop that directly affects ordering behaviors among fleet operators.
Therefore, as we transition into examining the trends surrounding Class 8 orders, it becomes clear that understanding the broader economic indicators, such as the TCI, is essential for grasping the challenges and decisions faced by stakeholders in this segment of the industry.
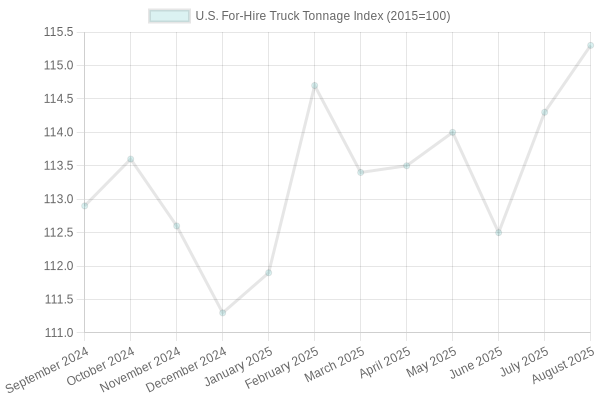
This graph showcases the U.S. for-hire truck tonnage index trends from September 2024 to August 2025, illustrating gradual growth amid economic fluctuations. The upward trajectory reflects improving freight volumes, critical for industry stakeholders navigating market uncertainties.
